
Once you have compared documents, simply make any further changes or revise any of the edited sections as required. Insertions and deletions are always tracked, but you can, for example, turn off ‘Comments’ here if you don’t want comments from the edited document to be included in the new version. You can then review these changes using the options under ‘Tracking’ and ‘Changes’ in the ‘Review’ tab.įor more control, you can also change the ‘Comparison settings’ via the ‘Compare Documents’ dialog box.
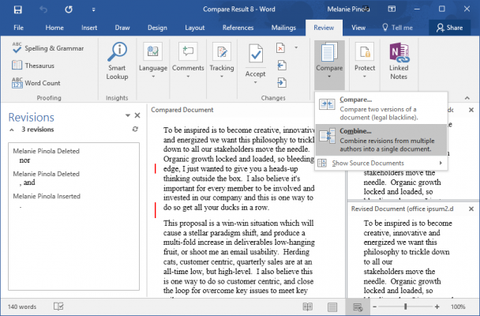
This will produce a new document with all the edits highlighted. Make sure ‘Word level’ and ‘New document’ are selected under ‘Show changes’ (these can be changed, but we find these settings work best in most cases).In the ‘Revised document’ box, select the edited version.In the ‘Original document’ box, select the older version of the document you want to compare (if it isn’t one of the listed documents, click ‘Browse’ to search for it).Go to ‘Compare’ and click the same option in the dropdown menu.Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox. To compare two documents, you need to go to the ‘Review’ tab on the main ribbon. This is similar, but it is designed to be used with documents that already have tracked changes in them. Microsoft Word also features a ‘Combine’ function. In addition, it is handy if you’re working on an essay and need to check where you made changes to previous drafts. This can be useful if someone has edited your work without indicating the changes. Essentially, all it does is take two copies of a document and marks changes as if they were made using ‘Track Changes’. What Is the Compare Function?Īs the name suggests, you can use the ‘Compare’ function in Microsoft Word to highlight the differences between two versions of the same document. As such, we thought we’d provide a quick guide to how it can be used.
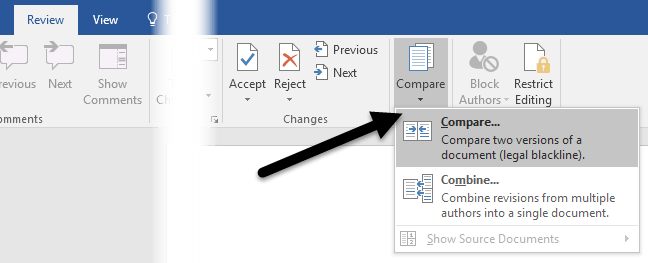
But it can be very useful when editing a document or redrafting an essay. Unless you’re a Microsoft Word expert, you may not have come across the ‘compare’ function.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
